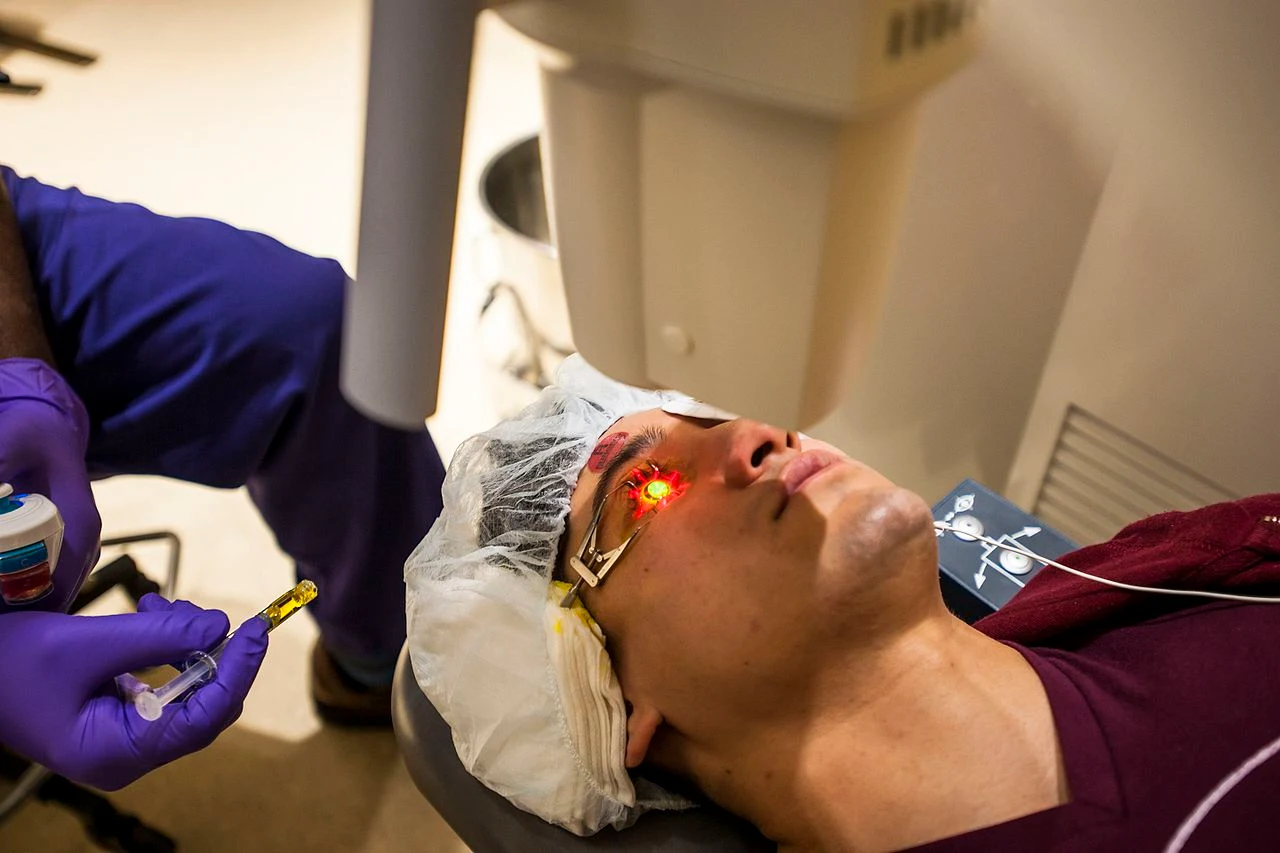
Corneal collagen crosslinking with riboflavin (vitamin B2) and UV-A light is a surgical treatment for corneal ectasia, such as keratoconus, pellucid marginal degeneration, and post-LASIK ectasia. it was first introduced in Germany in 1997 by Eberhard Spoerl and his team at the Dresden University of Technology.
The ultimate goal of a crosslinking treatment is to strengthen the cornea, which in turn slows or stops the disease's progression, but some patients will also see an improvement in the quality of their vision and a mild decrease in the amount of correction needed after treatment.
Crosslinking is generally a safe procedure, however, like any surgery, it is not without risks, its most common side effects are haziness of the cornea, punctate keratitis, corneal striae, corneal epithelium defect, and eye pain.
FDA has approved corneal collagen crosslinking for progressive keratoconus in April 2016. this approval only covers the crosslinking products developed by Avedro, which include Photrexa Viscous and Photrexa (riboflavin ophthalmic solution) and KXL System (UVA light source).
The FDA-approved method, also known as epithelium-off or epi-off, involves corneal epithelial debridment. after epithelial removal, 1 drop of riboflavin solution will be instilled topically on the eye every 2 minutes for 30 minutes. after that the eye will be examined under slit lamp for presence of a yellow flare in the anterior chamber, indicating adequate riboflavin saturation of the corneal tissue.
People undergoing crosslinking should not rub their eyes for the first five days after the procedure. patients may experience discomfort, foreign body sensation and may be sensitive to light, so sunglasses may helpful after the surgery. in case of severe pain in the eye or any sudden decrease in the vision, patients should contact their doctors. also if the bandage contact lens that was placed on the eye on the day of treatment falls out or becomes dislodged, patients should not replace it and must contact their doctors immediately.
Read more: Corneal crosslinking insurance coverage in the United States (2018).
The Fort Belvoir Community Hospital was the first military facility to perform this FDA-approved surgery to combat keratoconus. Photos by Reese Brown/DoD (PD)